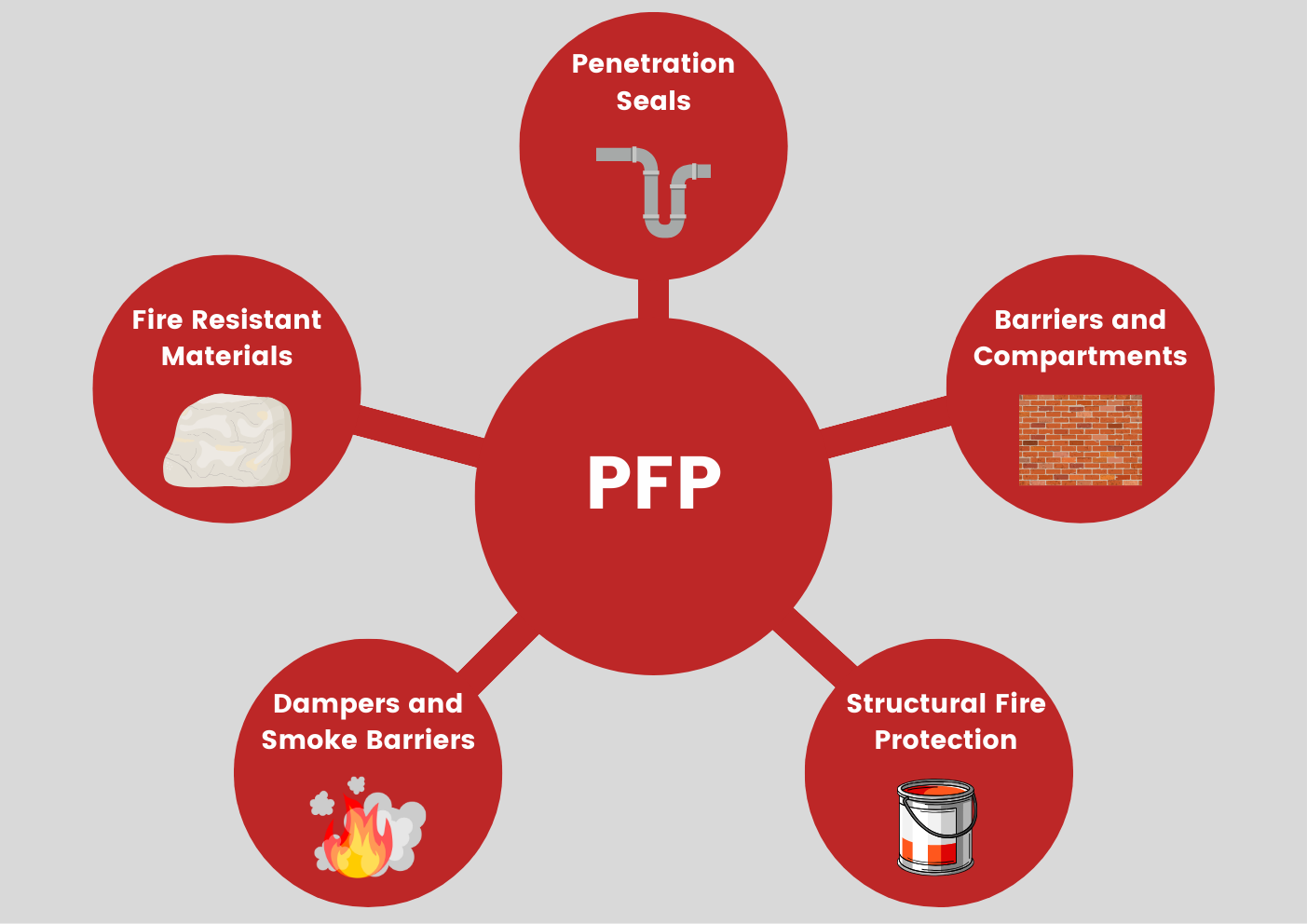
Passive fire protection (PFP) is a crucial component of any comprehensive fire safety strategy, designed to limit the spread of fire, smoke, and heat within a building without relying on active measures like alarms or sprinklers. This type of safety equipment includes fire-resistant walls, floors, and doors that act as barriers to contain fires and protect structural integrity. These elements are engineered to maintain their protective properties under fire conditions, ensuring that they do not change state when a fire occurs, which is vital for enhancing the overall safety of a building. One of the key challenges in maintaining effective passive fire protection is the presence of penetrations in walls and floors. During construction and throughout the life of a building, various services—such as electrical cables, telecommunications lines, pipework, and HVAC ductwork—often penetrate these fire-resisting barriers. If these penetrations are not adequately sealed with fire-stopping materials, they can serve as conduits for the rapid spread of fire, smoke, and toxic gases, undermining the integrity of the fire protection measures in place. Fire-stopping systems are specialized safety equipment designed to seal these penetrations, preventing fire from traveling through the gaps. These systems may include a variety of materials, such as intumescent sealants, fire-rated mortars, and pre-formed firestop blocks, each specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and maintain the fire-resisting capabilities of the surrounding structures.
Implementing effective passive fire protection and fire-stopping measures is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental responsibility for building owners and managers. Regular inspections and maintenance of fire-stopping systems are essential to ensure they remain effective over time, particularly as building modifications and service upgrades may create new vulnerabilities. In summary, passive fire protection and fire-stopping play a vital role in enhancing building safety and protecting lives. By incorporating robust safety equipment and ensuring that penetrations are properly sealed, property owners can significantly reduce the risk of fire spread and enhance the overall fire safety of their facilities.
 teknowfeed
teknowfeed