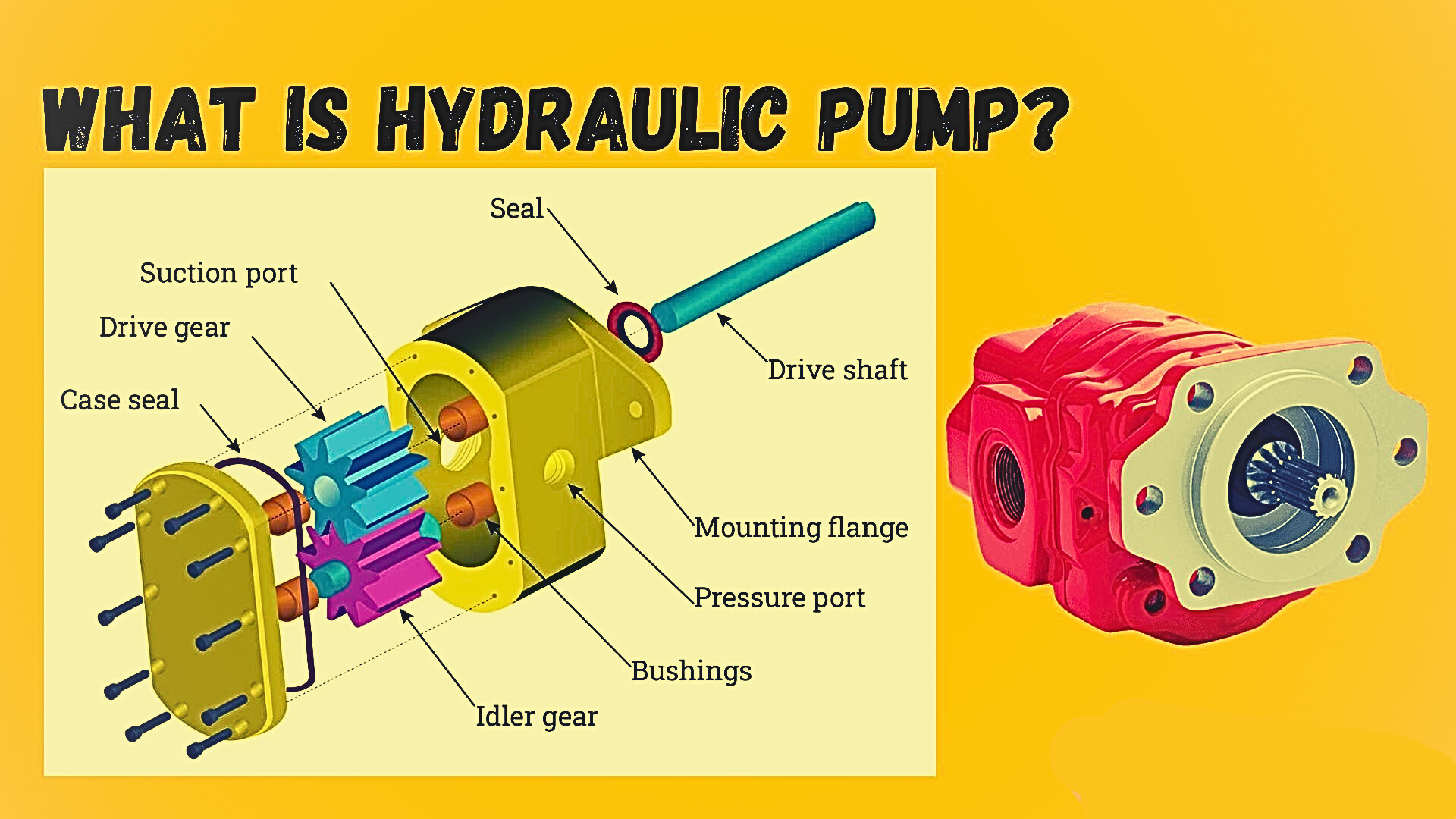
A hydraulic pump is an essential part of hydraulic systems because it moves pressured fluid through the system, transforming mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. Machines and other actions requiring a lot of effort, such pushing, lifting, or turning items, are powered by this pressurized fluid. Industries including manufacturing, construction, automotive, aerospace, and agriculture all depend on hydraulic pumps.
how hydraulic pump worksThe way hydraulic pumps work is by generating pressure and flow inside the system. A motor or engine transfers mechanical energy to a pump, which then transfers fluid typically oil from the pump's inlet to its exit. The system can move pistons, motors, or cylinders thanks to the pressure that results. The type of pump and its intended use determine the pressure and flow rate.
There are three main types of hydraulic pumps:Gear Pumps: These are simple, reliable, and cost-effective, often used in low-pressure systems. They consist of two interlocking gears that move the fluid.
Piston Pumps: Known for their high efficiency, piston pumps are used in high-pressure applications. They use a set of pistons to generate pressure and are commonly found in heavy-duty machinery.
Vane Pumps: These pumps use sliding vanes inside a rotor to create fluid flow and pressure. They are quieter and typically used in medium-pressure systems.
Applications and Benefits
Hydraulic pumps are widely used in industries that require powerful machinery and precise control. In construction, they power cranes, bulldozers, and excavators. In manufacturing, they are used in presses and conveyor systems. The main advantages of hydraulic pumps include high power density, reliability, and efficiency in transferring force over long distances.
Maintenance
To keep hydraulic pumps running efficiently, it’s essential to maintain fluid levels, change the hydraulic fluid regularly, and check for leaks or contamination. Proper care ensures long-lasting performance and reduces downtime.
 teknowfeed
teknowfeed